Focusing on data, we will obtain value and impact by computing while maintaining privacy and trustworthiness.
13
15
8
The group focuses on real-world solutions using computing technologies (cloud/edge, AI, blockchain, high performance, etc) in domains such as smart cities, health and energy, while managing the cloud data hub infrastructure at two sites: UiS campus and Green Mountain. The group ensures security and privacy remain paramount for the trustworthiness of any services and data management. DSComputing is part of the university's initiative on artificial intelligence – Stavanger AI Lab.
Partnership for joint Curriculum Development and Research in Energy Informatics (PACE)
PACE is a project under the Norwegian Research Council's INTPART programme.

The transition to a globally sustainable low-carbon emission society requires a significant increase in the use of renewable energy. We are facing increased decentralized energy production, and digitalization of the whole value chain.
Advanced use of ICT is crucial for realizing this energy shift. This is confirmed in the revised national strategy for Norway on energy research, Energy21 which recommends to give Digitalization and integrated energy systems top priority. In this context, the energy sector is facing two key challenges:
- The sector must be able to apply state-of-the-art ICT
- There is a lack of talents with the necessary expertise in the intersection between energy systems and ICT, which we refer to as energy informatics.
This project, which is a collaboration between research groups at University of Stavanger, University of Oslo, Technical University of Munich, and University of Lille, is one response to these challenges. The groups form the core of energy informatics educators and researchers at their respective institutions.
Energy informatics (EI) is an emerging interdisciplinary field that deals with the digitalization of the whole value chain of the energy sector. EI is concerned with how to exploit state-of-the-art ICT methods, tools and techniques to achieve sustainable energy generation and use. Research and education in EI requires a solid foundation in informatics. EI research and education can therefore naturally be envisioned as extensions of research and educational programs in informatics.
The goal of the project is to strengthen the research and educational activity on EI at the partner institutions.
Smart Community Neighborhood – driven by energy informatics (NFR EnergiX)
This project focuses on the development of mechanisms which will allow prosumers to share information about their production and consumption behavior.

It creates a decentralized virtual neighborhood where each household operates autonomously and trades energy with other households and communities, in which case, the central authority or the main grid only act as a facilitator. Such mechanisms will be particularly applicable for fluctuating loads and solving congestion problems.
The project aims to achieve this with ICT based smart-solutions. Machine learning based methods are used to learn and predict household production and consumption behavior. Incentive systems for energy trading are facilitated through the use of blockchains.
Furthermore, edge and fog computing drive energy information solutions. Finally, all technical components are driven by data privacy and security elements.
Kenya-Norway Mobility Programme for Computer Science Education
KeNoMo is a SIU/NFR NORPART project.

The objective of the project is to facilitate mutual student mobility and academic cooperation between the partners, and will thus enhance the quality of computer science education in both Norway and Kenya.
Cloud Artificial Intelligence for Pathology (CLARIFY)
CLARIFY is an EU ITN project.

CLARIFY’s main goal is to develop a robust automated digital diagnostic environment based on artificial intelligence and cloud-oriented data algorithms that facilitates whole-slide-image (WSI) interpretation and diagnosis everywhere with the aim of maximising the benefits of digital pathology and aiding pathologists in their daily work.
Read more about the project on the BMDLab page.
Future Energy Hub (NFR)
Future Energy Hub aims to create greener buildings and districts in collaboration with business and the public sector.

The project serves as a connection point for various disciplines. By connecting cutting-edge expertise from several fields, the best possible basis is created for innovative innovation and development towards greener cities.
Read more on Future Energy Hub's page (in Norwegian)
Digital Well Center (DigiWells)
Full name: Digital Well Center for Value Creation, Competitiveness and Minimum Environmental Footprint.

The objective of this NFR/SFI centre is to develop new knowledge, methodologies, and innovative solutions to improve the well delivery process enabled by digitalization, new sensors, high speed telemetry, automation, and autonomy.
Distributed fibre optic sensing for production optimization (DIFI-PRO)
DIFI-PRO is a NFR project.

This NFR project will perform experiments and modelling to increase our understanding of distributed fibre optic measurement systems as a cost-efficient tool for production optimization and increased field recovery.
5G Management and Orchestration for Data and Network Integration
5G-MODaNeI focuses on allocating together the network resources of 5G and the data resources of Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC).
The risks and the vulnerabilities for attacks and failures in 5G MEC will be identified. The impact of joint data and network resource allocation on security and dependability in 5G MEC will be determined. Next, innovative and intelligent solutions will be created. These solutions will allocate the network and data resources to maximize the security and dependability in 5G MEC.
Next Generation 3D Machine Vision with Embedded Visual Computing
The overall objective of this research is to give up the currently manual and time-consuming operational processes with well-composed digitalization using real-time 3D vision and learning processes.
This research aims to initiate an automated process deploying high-precision 3D sensing and online visual learning engines that operate in natural environments and are able to adapt in a holistic lifetime manner to changes during operations.
It targets establishing a groundbreaking technological concept for 3D machine vision as an interdisciplinary initiative linking cost effective and reliable depth sensing with advanced computer vision and embedded artificial intelligence to tackle challenges posed by time-varying visual scene perception in natural environments.
This research has a potential to a radical change in many parts of the value chain in the industry and society and selected scenarios will be designed for impact evaluation and opening up integration opportunities.
UiS will lead one of the work packages in the 3DSmartCam project: What are the capabilities and performance of the new 3D machine vision for digitalization of services and processes?
Automated Well Monitoring and Control
Well surveillance and control remain key issues for industries like oil and gas (O&G), geothermal, geological carbon storage (CCS) and compressed air energy storage (CAES).

Significant progress with real-time well measurements and automated data gathering has recently been achieved, while interpretation and well control optimization remain labour and time-consuming work mainly done manually.
The project aims at development and testing of a new methodology and tool (prototype software) for automated injection well monitoring and control based on real-time pressure, temperature and rate data. The basis is timelapse Pressure Transient Analysis (PTA) providing capabilities to monitor well performance and interference, containment of injected fluids and safety of abandoned wells.
Advanced interpretation and automation will be achieved via combining model- and data-driven approaches. Real field data will guide the project tasks and priorities and serve as a testing and application environment for the research and development. Automated well monitoring and warning system will be integrated with injection well control. The control includes rate changes designed to send signals with real-time interpretation of the response (on-the-fly well testing) to optimize well performance and interwell communication and prevent injection safety issues. The automated solution developed in the project will reduce costs, improve efficiency and minimize environmental footprint in O&G and facilitate CCS, CAES and geothermal industries.
UiS will lead one of the work packages in the Autowell project on prototype tool development.
NewbornTime
The NewbornTime project is about improved newborn care by using artificial intelligence (AI) for activity and event recognition in video from the time during and after birth.
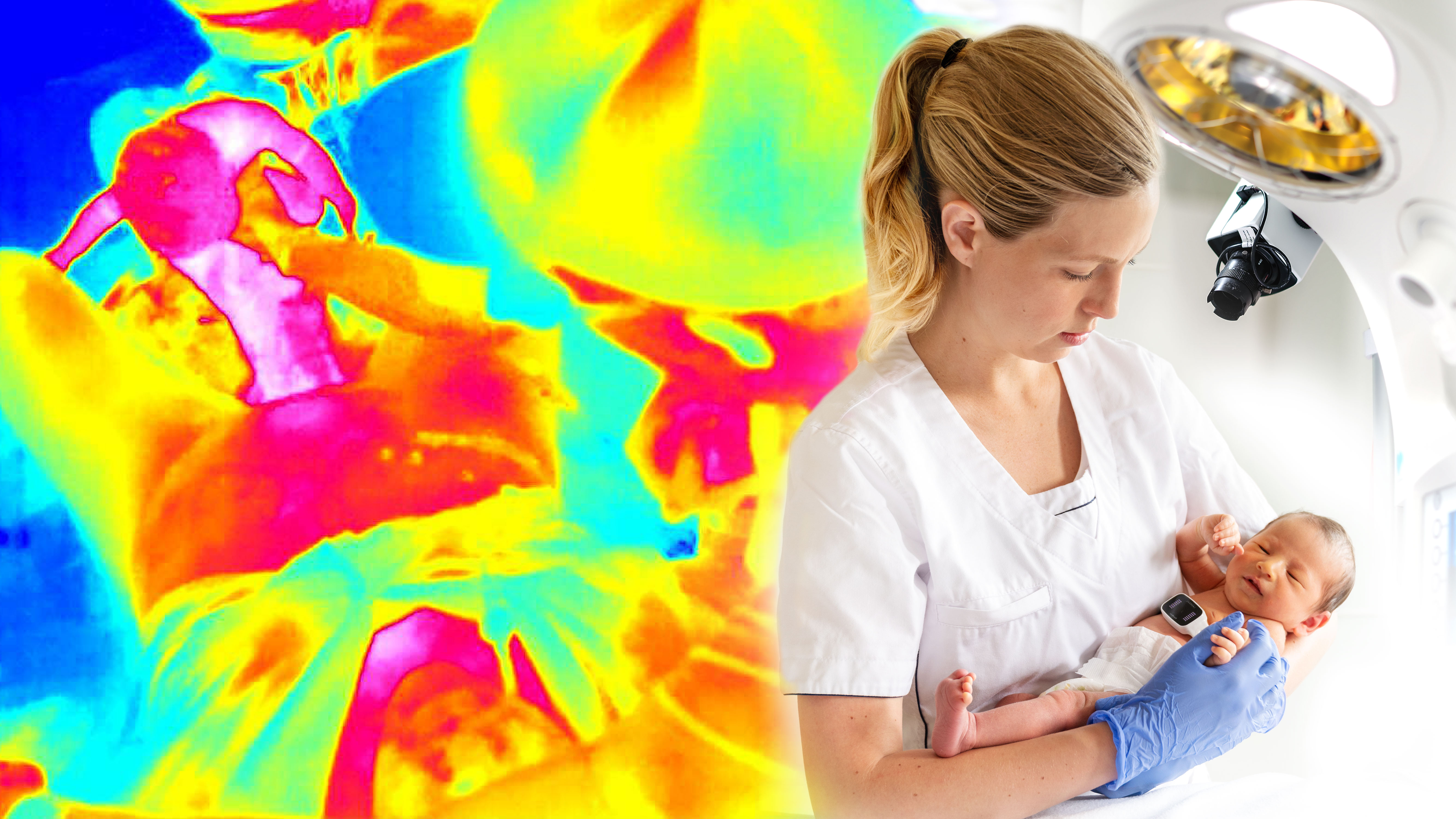

Deprivation of oxygen to an infant during and after birth might lead to birth asphyxia, one of the leading causes of newborn deaths, cerebral palsy and other long-term damage. According to guidelines, a newborn in need of help to start breathing should be resuscitated immediately after birth. Resuscitation activities include stimulating, clearing airways, and perform bag-mask-ventilation. In Norway, approximately 10% of term infants need stimulation and around 3% need bag-mask ventilation.
LAUNCH: Data-driven insights to boost the success rate and lifetime of retail food and beverage products
UiS researchers will collaborate with Foodback in a new project that will work to increase new products' chance of surviving in grocery stores.
Together with Professor Kai Victor Myrnes-Hansen (Norwegian Hotel College) and Professor Chunming Rong (Faculty of Science and Technology) Heidi Victoria Skeiseid is involved in the innovation project "LAUNCH: Data-driven insights to boost the success rate and lifetime of retail food and beverage products" . Over the next two years, the researchers, together with Foodback and Q-Meieriene, will look at how new products can more easily find their way onto people's shopping lists.
OpenIaC
A Plogen project on Open Infrastructure as Code.

To address the needs of modern information architectures, the OpenIaC (Open Infrastructure-as-Code) – “The network is my computing”, seeks to augment existing Cloud Computing and networking solutions with support for multiple cloud infrastructures and seamless integration of cloud-based microservices. The OpenIaC initiative seeks to provide a common open forum to integrate and build on advances in cloud computing and blockchain, creating of an open-source hub with fine-grained access control for an open and connected infrastructure of shared resources (sensing, storage, computing, 3D printing, etc.) managed by blockchains and federations, based on the principles of Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) among the federation of connected resources based on Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs). The initiative has the potential to provide a path for developing new platforms, business models, and a modernized information ecosystem necessary for 5G networks. The OpenIaC has a comprehensive new approach in all OSI layers from layer 2 up to applications that are built on underlying principles that include reproducibility, continuous integration/continuous delivery, auditability, and versioning. There are obvious needs to redesign and optimize the protocols from the network layer to the application layer. The solution includes a blockchain based decentralized and distributed technology for on-the-fly dynamic control framework on shared data as well as computing at edge, allowing a user to trace, retract, remove, and limit sharing of shared content. It gives the digital right and sharing control power back to the data creator, which is often considered as lost once it is shared today. It aims to create balance between data utility and privacy, thus creating a win-win situation between organizations and their customers.
More information could be found here soon: http://openiac.org/
Decentralized identity (DID)
Decentralized identity enables user-focused innovations in federated ecosystems with multiple service providers, in order to integrate digital technologies, knowledge, and data assets to become more responsive to citizens as well as improve digital services in a customized way.

This new decentralized infrastructure has great potential in addressing many issues of digital ethics and requirements by GDPR, including data ownership and usage, data quality, data protection and privacy, security and accountability, for managing industry data, public sector data, and personal data. Noticeably, major stakeholders in IT and banking have endorsed such research and innovations.
NCS2030
The research centre NCS2030 will find solutions that maximize the value creation of energy resources on the Norwegian continental shelf, while at the same time achieving the net zero emission (NZE) goals.

The vision of the NCS2030 is to be the scientific and technology driver to facilitate an energy-efficient, multi-purpose utilization of the subsurface into a “Sustainable Subsurface Value Chain” to reach the net-zero-emission goals.
Our researchers
Our PhD students
Related news
Laboratories for automation technology
The Faculty of Science and Technology at UiS has several laboratories within the field of automation technology. Here is...
NewbornTime – Improved newborn care based on video and artificial intelligence
The NewbornTime project is about improved newborn care by using artificial intelligence (AI) for activity and event reco...
Among Norway's foremost women in Artifical Intelligence
Professor Kjersti Engan is listed as the 11th most influential woman in the field of artificial intelligence.
UiS establishes an interdisciplinary research group within tunnel safety
Aiming to promote innovation and achieving increased tunnel safety, a research group has been established at the Departm...
How to collaborate with Stavanger AI Lab?
Stavanger AI Lab opens up for several types of collaboration with society. We see it as our social mission to raise comp...
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science is responsible for teaching, research and development within e...

























